Problem-solving with creative design
How to develop a design thinking and innovation strategy in digital product development.

Nowadays designers look forward to providing shapes, forms, and uses that connect ideas with key functionality and contribute to social changes, taking advantage of technology benefits that we need in UX/UI, or experience, development. They optimize the results using design and critical thinking as well as integrated tools and strategies for the construction of the design of those digital products.
George Eastman, founder of Eastman Kodak Company in 1892 said, “dreams are limited only by imagination.” The creative problem has a solving system if you’re able to pass that limitation.
Today, design involves technology to solve more complex usability problems. The amount of data required to solve problems has increased rapidly in this century. The design problem-solving process may need larger teams with more diverse members from different fields. Teams need to combine skills in order to solve the issue to bring design and innovation solutions together.
The product design objective process
The product design objective process is divided into 4 steps.

- Contribute to social changes: This means knowing the society where you want to put a product for use. Proposing changes and supporting commitment in between teams, clients, users, and the tools you’re using.
- Formalizing intentions: Where you add value connected to the reference of the society; making pieces that can be a more equal or balanced product.
- Giving form to uses: Making a better UI/UX system you optimize the efficiency and interfaces. Adapting uses to contemporary needs
Taking hold of technologies: Integrating techniques and technologies while limiting environmental impact.
1. Contribute to social changes
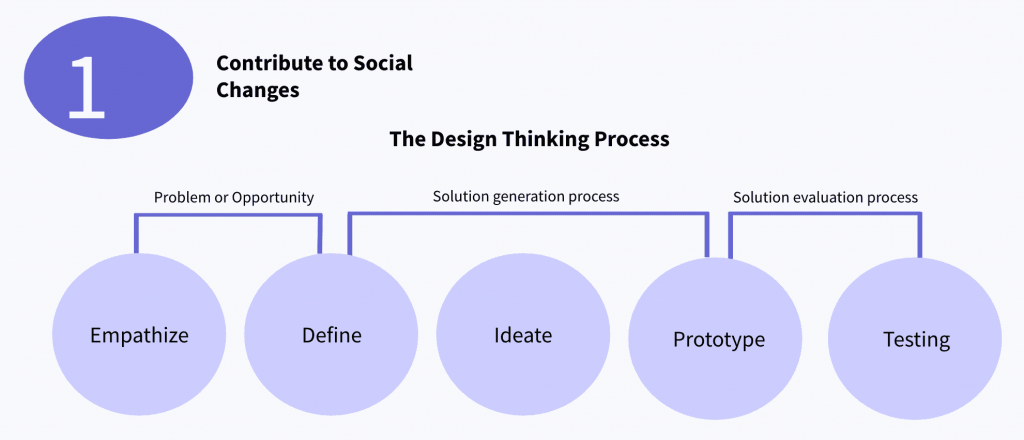
Problem or opportunity
- Emphasize: Researching and interrogating society and user needs.
- Define: Defining those elements and propose changes according to users’ and society needs. Creating a design brief, noting the design parameters.
Solution generation process
- Define: Part of the solution generation process because through the definition you go to the ideation stage where you create ideas and select better design parameters for innovative opportunities and development.
- Ideate: Create ideas and select better design parameters for innovative opportunities development.
- Prototyping: Start creating solutions more tangibly. Visualizing and storytelling.
Solution evaluation process
- Prototyping: Interactive design and prototyping.
- Testing: Validating the solution, refining results, and incorporating constructive feedback.
This is a process of emphasizing research and ideation which helps designers move to prototyping product development. It also allows you to have a very clear and defined ideation process.
2. Formalizing intentions in the design thinking process
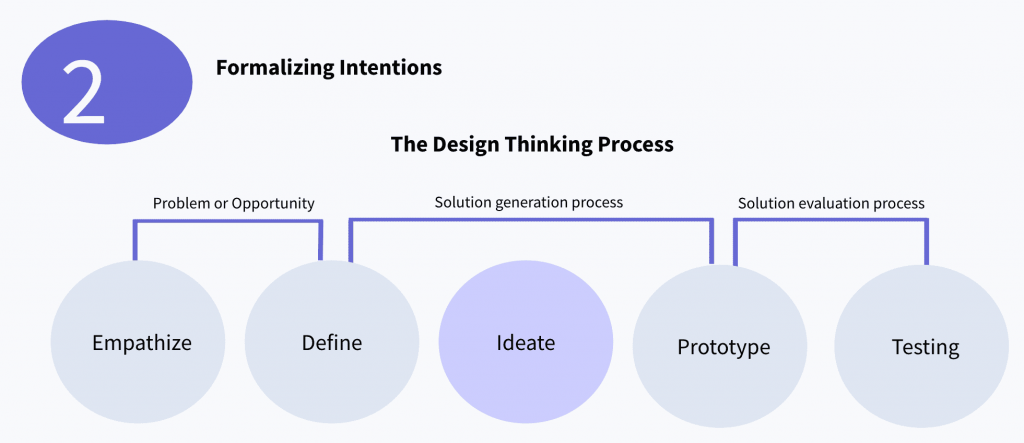
When you are in the ideation step, as mentioned above, you create ideas and select better design parameters for innovative opportunities development.
Start with a problem, analyzing three elements:
- Technology: The main element; it gives you the tools to address this problem or opportunity
- Business: Business is focused on viability, making sure it is possible on the business side
- User. Last, but not least there is the user and the desirability
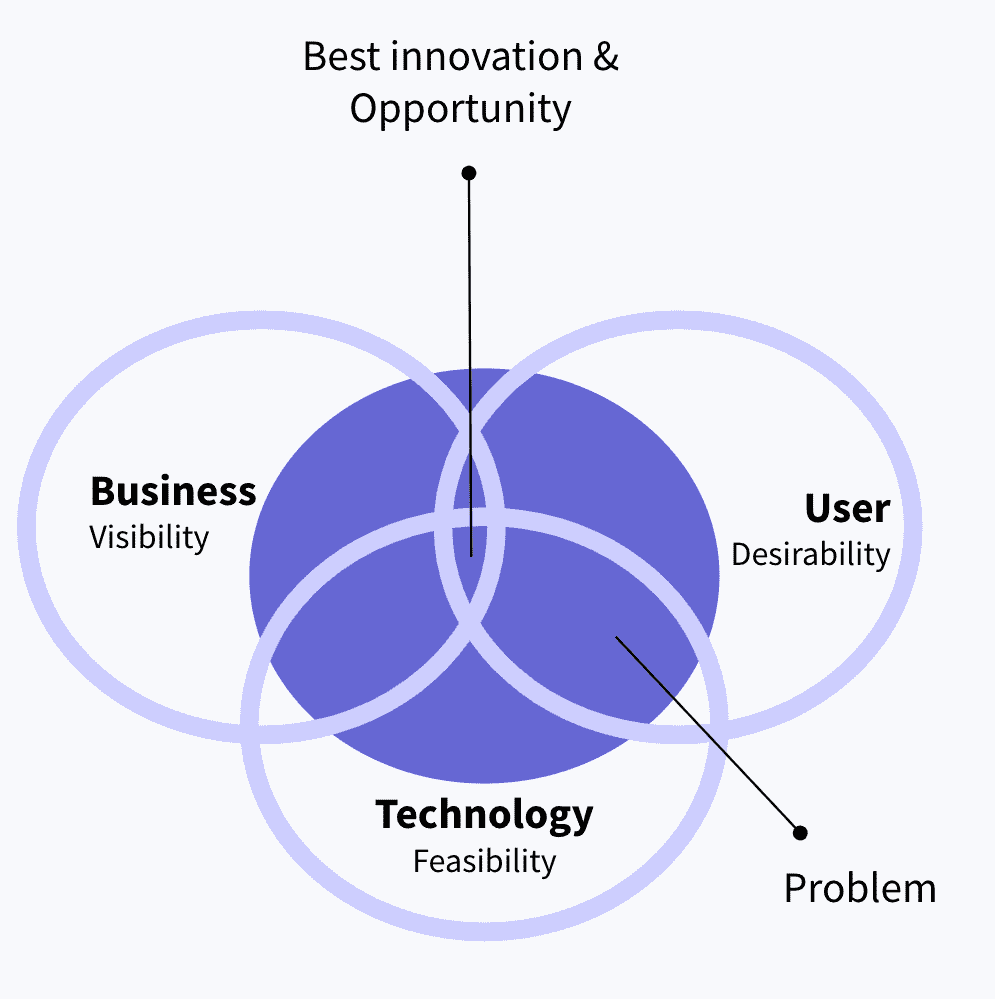
The design process begins with establishing a connection and understanding of the end user and the market in which the product will be positioned. Start by considering two perspectives:
- Feasibility: Focused on technologies and tools they can use to address a need or opportunity
- Viability: Focused on a given business strategy of a financial target
While these are important, they ignore desirability, or who the user is, what they care about, and why. Design thinking is often referred to as human-centered design because designers always start their approach by looking at the people and their needs before considering feasibility and viability. Merging these three elements you will find the best opportunity in the market.
The divergent, convergent ideation process
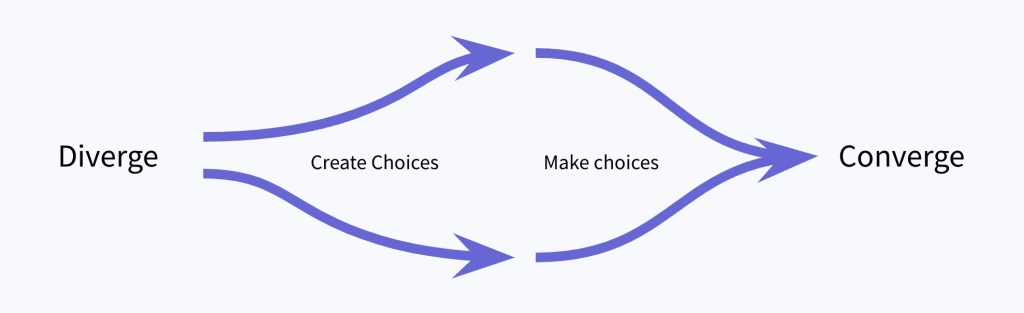
Diverge to explore new possibilities:
- Gather a wide range of stimulus and ideas.
- Use a deck of creative prompting cards.
- Brainstorm with colleagues who aren’t working on the project.
- Document every idea.
Converge to focus on the best route forward
- Refine ideas and recognize patterns.
- Establish evaluation criteria.
- Force yourself to answer if you had to do it now.
- Prioritize.
- Sketch ways of structuring your problem.
- Give it some space.
Consider: What concept is most likely to resonate with our consumers? Which project approach is most likely to meet our team’s goals? Do certain ideas align more with company strategy?
Explore a range of options before selecting the best path forward
- The divergent-convergent process is at the heart of all projects.
- The usability of this structure is that it applies in any time frame of the project.
- The main point is to recognize which behavior you might need at any moment.
- You have too many options and you’ve been looking for the main direction.
Consider: Projects that create new value have periods of uninhibited exploration followed by critical organization and refinement. You could use it in an afternoon meeting, several times in a one-week sprint, or routinely across a two-month project. Are you stuck in a rut on the project? Then explore new options through divergent thinking. Force yourself to edit and prioritize so you can work on something more specific.
One great example is the Sony PlayStation 5. It is a combination of all the experiences they had as a product, in terms of industrial design, digital prod dev, and UX/UI dev, that delivers a product that simplifies user interaction.
3. Give form to users
Optimizing uses according to functionalities, performance and efficiency. This is something that needs to be merged in the user interaction and UX development. It is also important to consider users in the design process adapting to them and making it more accessible.
A great example is the integration of Slack with Salesforce. They considered the end-user in the design process, adapting to that end user’s needs and making it more accessible. Making interaction easier.
4. Taking hold of technologies

In this step, you use technologies as an advantage for the development of products.
As an example, Salesforce and Salesforce Trailhead offer integration of techniques and technology development. They improved the existing functionality and converted intangible ideas to tangible solutions, simplifying access to technology.
Details that matter in UX/UI development and the design innovation process:
- UX is not only UI, the interface is part of the experience.
- Know your audience, you are not the main user of the product.
- Adapt the designs for short attention spans.
- The design simplifies the UX/UI.
- Adapt the design process according to the product you are designing.
- Ideate and prototype before constructing the final product.
- Use real content while you are designing.
- Make a simple and consistent design layout.
- Recognize overall patterns and impact in the design process.
- Make design accessible and inclusive.
- Don’t try to solve a problem by yourself or everything at once.
- Preventing errors is better than fixing them.
- Receive informative feedback.
- Avoid dramatic redesigns.
Suggested Trailhead Trails:
- Innovation Ideation & Prototyping
- Design Thinking for Sales
- Innovation Project Definition
- Lightning Design System Basics
- Develop for Lightning Experience
- Innovation Basics
- Designing for Web Accessibility
- App Design and Prototyping
- Innovation Solution
- Lightning Design System Trailmix by Andrea G
- Design Innovation Trailmix by Andrea G

